TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS:
BENEFITS, CONSIDERATIONS, AND USER RIGHTS
by Thulasy Suppiah, Managing Partner
Traffic Management Systems (TMS) are becoming increasingly vital in modern urban planning and infrastructure. These systems use a combination of sensors, cameras, and data analysis to monitor and manage traffic flow, reduce congestion, enhance road safety, and provide real-time information to both traffic authorities and road users. As cities grow and transportation demands increase, understanding the benefits and implications of TMS is crucial for stakeholders, including solution providers, users such as highway operators and government entities, and individual road users.

BENEFITS:
1. Improved Road Safety:
TMS enhances safety by identifying pedestrian and vehicle movements, employing intelligent signaling techniques, and automatically managing incidents. Real-time monitoring helps in detecting accidents and hazards, allowing for quick responses. Systems alert drivers to potential hazards like closed roadways or low visibility, encouraging safer driving practices.
2. Reduced Traffic Congestion:
One of the primary goals of TMS is to alleviate traffic bottlenecks. By using real-time data on traffic conditions and intelligent traffic control techniques, TMS optimizes traffic flow. Predictive analysis helps identify congestion-prone areas and redirect traffic accordingly.
3. Reduced Fuel Consumption and Emissions:
Efficient traffic control systems can lower fuel usage and vehicle emissions. Consistent traffic flow enables vehicles to maintain steady speeds, improving fuel efficiency. Strategic route development and congestion avoidance contribute to a more sustainable and ecologically friendly urban transportation landscape.
4. Improved Emergency Response Times:
TMS enables emergency vehicles to navigate congested areas more efficiently. Prioritizing routes using smart traffic lights and creating green corridors ensures that emergency services can reach their destinations faster, supporting rescue and emergency operations effectively.
5. Better Public Transit:
TMS prioritizes public transportation by optimizing transit routes, leading to improved service and increased ridership. This integration reduces traffic congestion and enhances transportation efficiency.
6. Decreased Noise Pollution:
By streamlining traffic flow and minimizing the need for frequent braking and acceleration, TMS helps reduce noise pollution. Smoother traffic patterns lead to quieter roadways.
7. Enhanced Accessibility for Pedestrians and Cyclists: Intelligent traffic arrangements provide dedicated lanes for cyclists and extended crossing times for pedestrians, promoting safety and convenience for non-vehicular road users.
8. Predictive Insights:
Smart traffic management systems offer predictive insights by analyzing data collected from traffic sensors. This data assists governing bodies in understanding roadway usage and making informed decisions.
CRITICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR STAKEHOLDERS:

For Solution Providers:
Data Security and Privacy
Ensure that the TMS complies with data protection regulations, safeguarding user data from unauthorized access and misuse.
System Reliability
Implement robust testing and maintenance protocols to ensure the system operates reliably under various conditions.
Scalability and Adaptability
Design the system to be scalable and adaptable to future technological advancements and changing traffic patterns.

For Users (Highway Concessionaires, Government/Agencies/Town Councils):
System Integration
Ensure the TMS integrates seamlessly with existing infrastructure and other smart city initiatives.
Training and Support
Provide comprehensive training for personnel to effectively operate and maintain the TMS.
Performance Monitoring
Regularly monitor the system's performance to identify areas for improvement and optimization.

For Road Users:
Awareness of Rights
Understand your rights concerning data collection and usage by TMS and be informed about how traffic data affects route planning and traffic enforcement.
Safety and Compliance
Adhere to traffic regulations and be aware of real-time information provided by the TMS to ensure safe driving practices.
Feedback Mechanisms
Utilize available channels to provide feedback on the TMS, helping to improve its effectiveness and user experience.
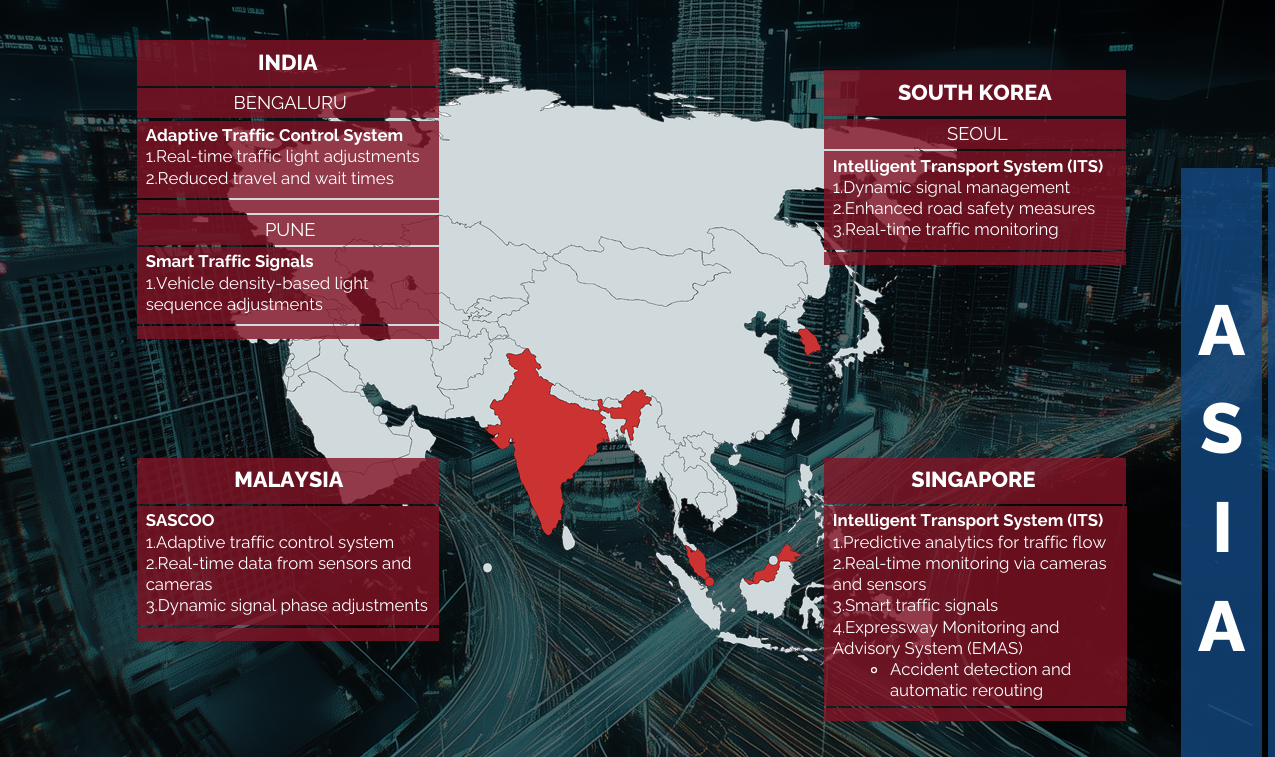
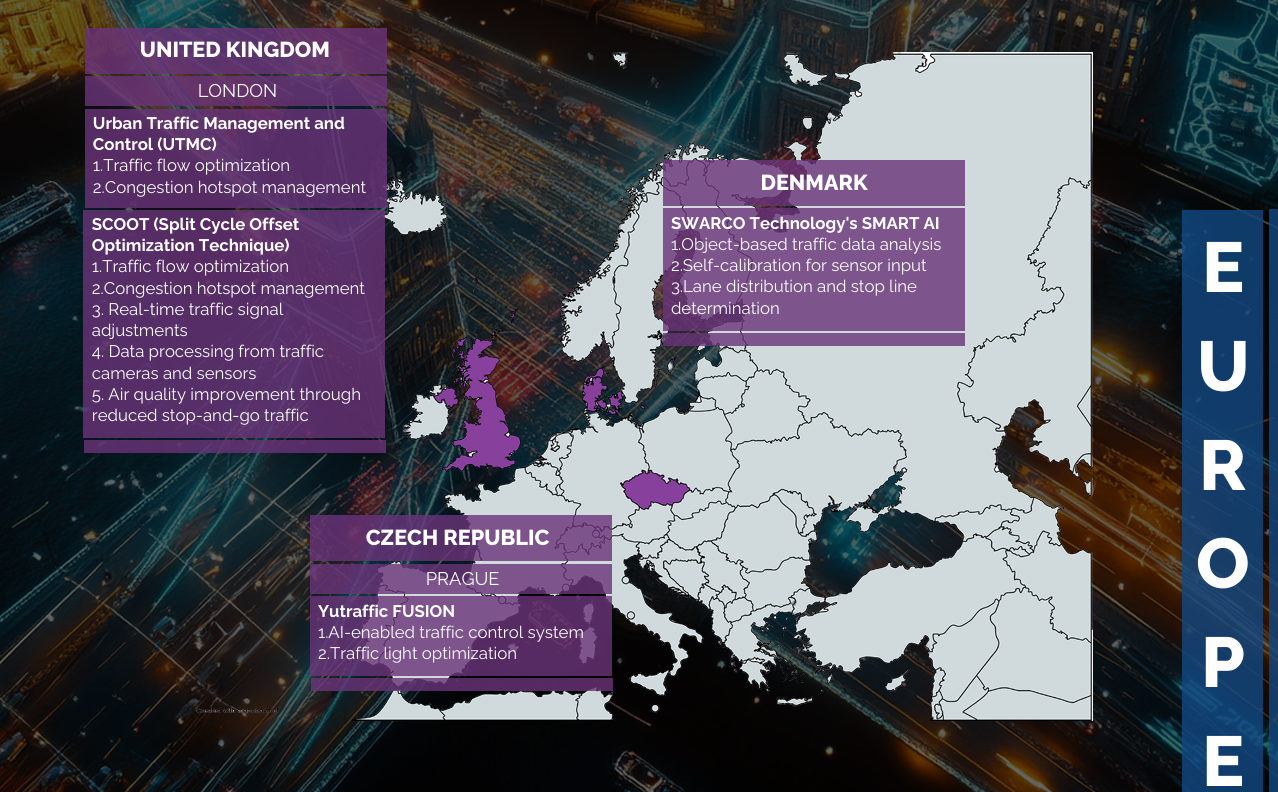
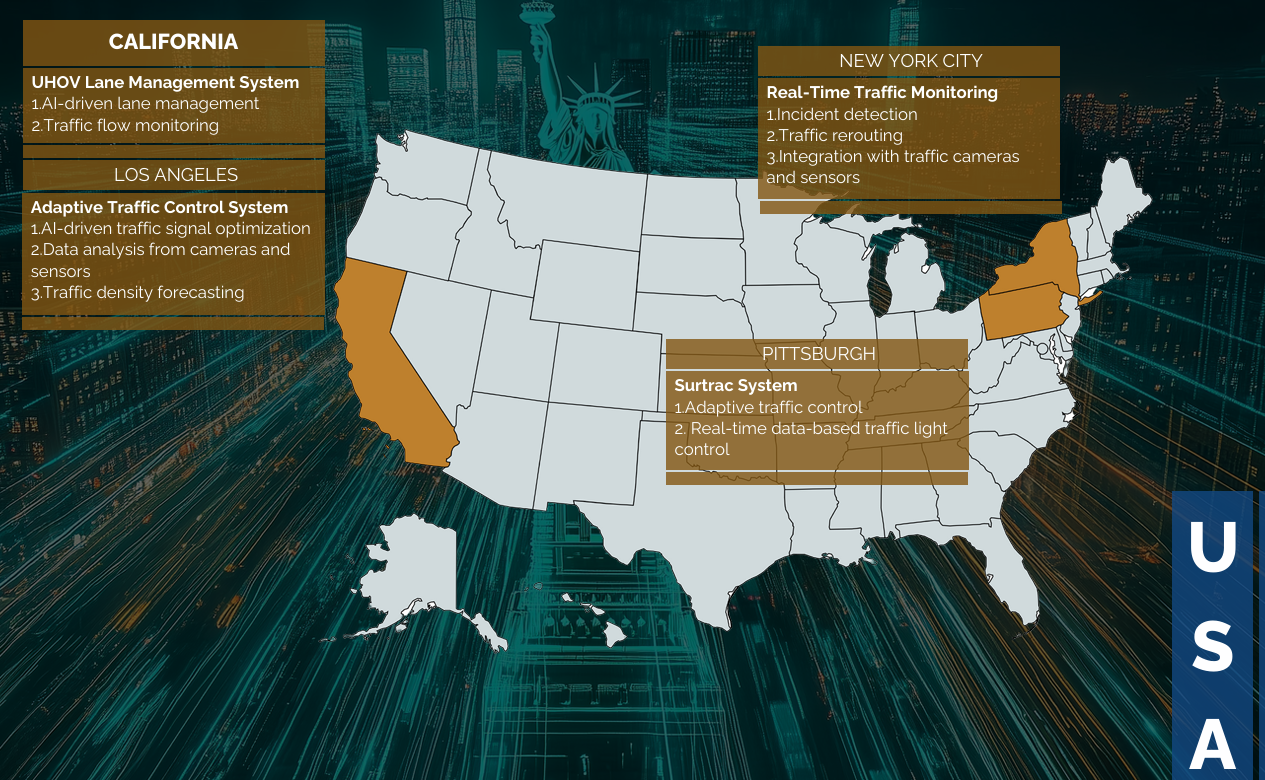
EXAMPLES OF AI IN TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
Conclusion:
Traffic Management Systems offer numerous benefits, from enhancing safety and reducing congestion to improving environmental sustainability and emergency response times. However, successful implementation requires careful consideration of data privacy, system reliability, and stakeholder engagement. By understanding the benefits, considerations, and user rights associated with TMS, stakeholders can work together to create more efficient, safe, and sustainable urban transportation systems.
References
- https://www.parknsecure.com/top-3-benefits-of-advanced-traffic-management-system/
- https://keegangroup.com.au/7-benefits-of-effective-traffic-management/
- https://www.matellio.com/blog/smart-traffic-management-system/
- https://www.symmetryelectronics.com/blog/what-is-a-smart-traffic-management-system/
- https://eastgate-software.com/exploring-the-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-intelligent-traffic-systems/
- https://trakblaze.com/insights/exploring-the-benefit-of-the-traffic-management-system/
- https://hatfieldandassociates.com/maximizing-efficiency-the-five-benefits-of-a-transportation-management-system/
- https://www.warehousingandfulfillment.com/warehousing-and-fulfillment-resources/transportation-management-systems-11-key-features-benefits/
- https://redresscompliance.com/ai-in-traffic-management/
- https://www.swarco.com/stories/ai-based-traffic-management
- https://hyscaler.com/insights/ai-in-traffic-management-5-effective-ways/
© 2025 Suppiah & Partners. All rights reserved. The contents of this newsletter are intended for informational purposes only and do not constitute legal advice.
More Newsletter
REACH US
SUPPIAH & PARTNERS
(Formerly Law Office of Suppiah)
(Main Branch)
UG-13, LEXA Galleria,
No. 45, Jln 34/26, Wangsa Maju
53300 Kuala Lumpur,
Malaysia
+03 41420675
+03 41423766
+03 41313908
NAVIGATION
ARTICLES
- COPYRIGHT © 2025 SUPPIAH & PARTNERS (Formerly Law Office of Suppiah) ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
- HTML SITEMAP
- PRIVACY POLICY